Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of absorbable anti-adhesion membranes
Chen Zao-mei 1, 2, 3, Li Ru-bing 1, 2
- 1 Department of Pharmacy, Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; 2 Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Rational Drug Use for the Elderly with Chronic Disease, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; 3 Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2017-02-13Online:2017-06-28Published:2017-07-07 -
Contact:Li Ru-bing, M.D., Chief technician, Department of Pharmacy, Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Rational Drug Use for the Elderly with Chronic Disease, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Zao-mei, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Pharmacy, Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Rational Drug Use for the Elderly with Chronic Disease, Guangzhou 510010, Guangdong Province, China; Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Production and Research Projects of Guangdong Province, No. 2012B091100170; the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, No. 201509010012
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Zao-mei, Li Ru-bing. Research progress of absorbable anti-adhesion membranes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.18.021 .
share this article

2.1 可吸收防粘连膜 2.1.1 粘连 粘连是结缔组织纤维带与相邻的组织或器官结合在一起而形成的异常结构。组织粘连是外科手术后常见的临床现象和患者愈合的必经过程,若在腹腔、盆腔等手术中出现粘连现象,则会引起小肠梗阻、继发性不孕症和腹腔、盆腔疼痛等多种并发症。粘连所引起的严重并发症需要手术治疗,而且粘连的发生会增加后续手术的难度,导致手术时间延长、术中出血增多、周围组织器官损伤概率增加,甚至使腹部放化疗和再次手术的难度和风险显著增加,加重患者的痛苦和经济负担,所以预防术后粘连的发生是毋庸置疑且意义重大的。 2.1.2 可吸收防粘连膜材料 对于可吸收高分子材料的研究,最早是在20世纪60年代。在1965年人们便开始不断地尝试用可吸收材料来代替传统材料,然而却不能满足临床的要求。在20世纪80年代,因高分子聚合技术的发展尤其是纤维增强技术的引进才使得可吸收高分子材料在临床的应用成为一种可能。可吸收材料在国内外得到广泛应用是在20世纪90年代后。 早期防粘连膜材料的缺点是不易降解,并且需要二次手术取出,使患者难以接受。目前抗腹腔粘连的材料主要是物理屏障类材料(固体和液态制剂),液态类抗腹腔粘连屏障材料通过“漂浮作用”使创面互相分离而避免粘连的发生[4],研究发现此类材料无法起到防粘连作用,且会影响腹腔内的正常生理生化过程[5],临床研究也表明液态材料因在体内停留时间过长而容易形成新的粘连[6]。固态类抗腹腔粘连材料因难以固定于受创区或易黏附在潮湿的环境中而使其在实际应用中具有一定的局限性。 天然高分子化合物作为膜材料具有良好的降解 性[7-8](图2),这些术后防粘连产品都具有降低粘连复发率、良好的隔离作用、良好的生物降解性以及良好的组织黏附性、良好的生物相容性等特点,可有效防止术后粘连的发生,但在制膜时多采用流延成膜法[9-10],该方法制得的防粘连膜仍存在脆性大、韧性差、纤度不够、柔软性差及力学性能差等缺陷,然而利用静电纺丝技术将该类材料进行静电纺所制得的防粘连膜具有柔软性高、组织黏附性好、组织相容性高等优点,很好地克服了传统制膜方法的不足,用该方法制得的薄膜在组织愈合过程中不但起到防粘连作用,且在术后可自行降解或被吸收,避免了二次手术的痛苦,是非常好的医学生物膜。 可见,优质可吸收防粘连膜材料需加以借助优越性极好的静电纺丝制备技术才能更好地发挥其防粘连的疗效特性。"


2.1.3 国内外可吸收防粘连膜产品及特点 当前国内已拥有40多种术后防粘连产品(图3),首个由国家食品药品监督管理局、美国食品和药物管理局以及欧盟安全认证机构认证的防粘连产品Seprafilm,是由透明质酸通过酯化、交联、接枝等化学修饰制得[11],适用于骨盆剖开或腹部手术,具有很好的生物可吸收性和组织相容性,可安全有效地降低粘连相关的发病率,且操作简便。 采用壳聚糖为膜材料研制的可吸收性术后防粘连膜[12],其适用范围广泛,具有很好的生物相容性和降解性,具有促进伤口愈合、抗溃疡及杀菌等生物活性。如:烟台某医用品有限公司开发的以壳聚糖为原料的粘停宁,适用于妇产科手术、腹腔手术、骨科肌腱手术,能有效降低术后粘连复发率、促进手术后器官功能的恢复,在一定程度上缩短了患者的住院时间。北京某生化有限公司以改性壳聚糖生产的“百菲米”防粘连膜适用于腹腔镜手术,可减少术后肠粘连的形成[13],放入体内后在很短时间内便与体液互相作用。虽然该产品具有良好的生物隔离作用,但其降解较为缓慢。在国家药品不良反应监测中心可疑不良事件(共171例,其中严重伤害占24%,其他占76%)的报告中揭露壳聚糖产品所发生的可疑群体医疗器械不良事件给此类产品的安全性带来了质疑[14-15]。 采用聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物所制成的防粘连膜应用也日益广泛。如:重庆一生物药业股份有限公司用聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物为原料生产的“诺奇”可有效防止腹腔内肠、肝脏等脏器的粘连。某大学生物材料工程研究中心研发的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物可吸收术后防粘连膜,在有效防止脏器术后粘连的同时,也能防止硬膜瘢痕和肌腱的粘连。对94例宫腔粘连患者应用此类防粘连膜的效果进行研究,发现使用该类防粘连膜可形成屏障阻隔子宫前后壁,避免再次粘连的出现而利于子宫内膜创面的愈合[16]。但是此类生物可吸收防粘连膜柔软性不高[17],组织黏附性差而需要通过缝合固定。 用聚-DL-乳酸制备的可吸收性防粘连膜能有效地防止肌腱和腹部等部位手术后粘连的发生[18-19]。上海某生物科技有限公司生产的“粘克”适合防止外科术后粘连的发生,且安全、疗效好[20]。成都一生物医学材料有限公司生产的“DKFILM”可明显提高腰椎间盘术中远期优良率从而降低腰椎术后综合征的发生率,显著减少术后粘连的发生。石家庄市一生物医学材料有限公司生产的“瑞术康”不但能有效预防粘连,且拥有良好的生物降解性能,其制造成本也较低,减轻了广大病患的经济负担。黑龙江某科技有限公司的“粘连平”可吸收医用膜,具有疗效显著、无任何不良反应的优点,它对肝肾功能等均无影响[21-22]。 国外已被FDA认可的医疗器械行业防粘连产品有4种[23]:Interceed,Adept,Seprafilm,Surgiwrap。虽然产品广泛应用于临床和研究中,但仍存有不足:Interceed在有腹膜液和血液环境下时,其有效性有限;Seprafilm用于手术时,要求较为严格,其操作性差,需尽可能地止血;Adept用于手术部位时,会有液体外渗导致患者的不适;Surgiwrap作为术后防粘连膜需要进行缝合固定,并且面临着发生再次粘连的风险。 国外的防粘连产品具有很大的优越性[24],如某外科产品公司出品的Seprafilm生物可吸收防粘连膜具有降低术后组织粘连发生率以及缩小粘连发生范围的优点,临床上的广泛应用也表明了其安全有效性;日本公司生产的“赛膜”应用于硬脑膜缺损的修补,能有效减少粘连的发生;强生公司的Interceed防粘连膜可有效防止术后粘连并且安全不引起任何并发症。 虽然目前临床上应用广泛的可吸收防粘连膜有较强的防止术后组织粘连的作用,现开发的生物可吸收防粘连膜也越来越功能化,但都存在缺陷,尚未达到理想要求,需致力于寻找一种技术来研发新型可吸收防粘连膜,克服当前可吸收防粘连膜所存在的不足,这也应是医学领域上的热点与重点。"
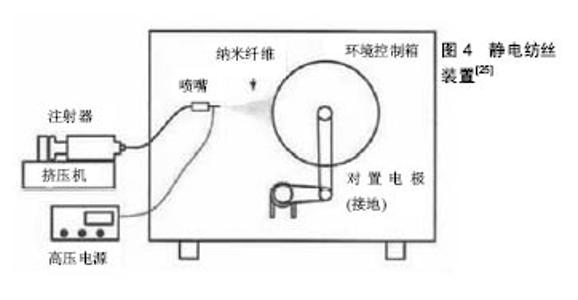
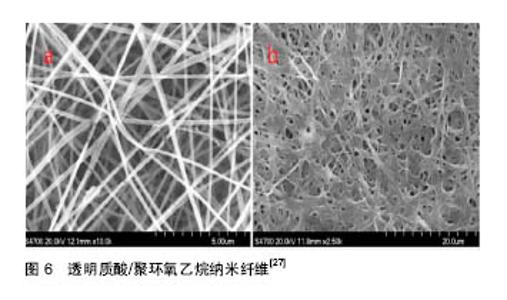
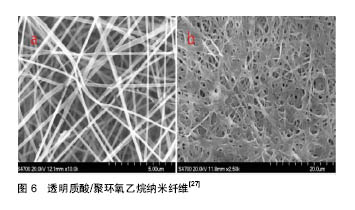
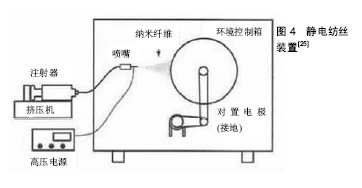
2.2 静电纺丝 2.2.1 静电纺丝过程 静电纺丝是一种直接制备纳米纤维的方法,主要由高压电源,溶液储存装置,喷射和接收器装置组成(图4)[25]。相对应可以分为5个过程:流体带电、泰勒锥的形成、射流的细化、射流的不稳定和纤维的接收。 静电纺丝主要是利用高压电源装置在注射器的金属针头与接收装置产生电位差。当高压电场开启时,聚合物溶液表面产生电荷,由于电荷相互排斥作用,会产生一种与表面张力相反的静电引力。电压不够大时,静电引力不足以克服液滴的表面张力,液滴仍然悬挂于喷丝口。当外加的电压增大时,即将滴下的液滴形成Taylor锥。继续加大外加电压,当电压超过某一临界值时,静电引力大于表面张力时,液滴将形成一股带电的喷射流从喷丝口喷出。在电场的作用下,射流的比表面积迅速增大而使溶剂快速挥发,最终被收集并固化形成纳米纤维膜(图5,6)[26-27]。 2.2.2 静电纺丝在医学领域的应用 自静电纺丝技术崛起,静电纺丝纤维的应用前景使得这技术在国内外引起了广泛的关注。纳米纤维的直径小于细胞,可以模拟天然细胞外基质的结构和生物功能;人的大多数组织、器官在形式和结构上与纳米纤维类似,为纳米纤维用于组织和器官的修复提供了可能;静电纺原料具有很好的生物相容性及可降解性,可作为载体进入人体,并易被吸收;静电纺纳米纤维有大的比表面积、孔隙率等优点使得静电纺丝技术在生物医学领域中有巨大的应用前景,包括组织工程、人造血管、组织修复、伤口包扎制品、药物载体等方面。Bagherzadeh等[28]将聚己内酯溶解在三氯甲烷和甲醇中进行静电纺丝,采用激光共聚焦显微镜和三维图形分析技术对纤维支架的多孔结构和孔径参数进行分析,结果表明该纤维支架具有较好的孔连通性和多孔结构。随后,Nguyen等[29]用成纤维细胞和内皮细胞再次验证了电纺聚己内酯纤维支架具有良好的细胞相容性,使得其可作为组织工程支架为细胞的生长和增殖提供支撑。 2.3 静电纺丝技术制备的防粘连膜 2.3.1 静电纺丝法制备可吸收防粘连膜的优点 利用静电纺丝技术制备纳米纤维材料是近十几年来世界材料科学技术领域的最重要学术与技术活动之一[30]。自20世纪90年代起,静电纺丝凭借其制造装置简单、纺丝成本低廉、可纺物质种类繁多和工艺可控等优点,成为了有效制备纳米纤维材料的主要途径[31-32]。目前利用静电纺丝技术所制备的可吸收医用生物膜集合了该技术孔隙率高、低密度、强度性好等优势。姚清华[33]以RGD-重组蛛丝蛋白pNSR16及聚乙烯醇PVA-124为原料,用静电纺丝技术制备纳米纤维膜,用于修复烫伤,研究发现,制备出的防粘连膜不但具有表面积大、孔隙率高、纤维纤度细以及良好的机械强度等优良特性,而且具有适宜的柔软性、适宜的组织黏附性以及良好的生物相容性。各国医务人士倾向于使用术后免缝合固定且可自行降解或吸收的防粘连膜,借助静电纺丝技术所制备的可吸收防粘连膜恰好满足了临床上对这一方面的需求。 2.3.2 现有的静电纺可吸收防粘连膜产品及其特点 现有的静电纺可吸收防粘连膜产品具有良好的生物相容性和生物活性、良好的组织黏附性、良好的柔顺性、较高的断裂伸长率等特点,在有效防止组织部位术后粘连发生的同时具有促进细胞再生作用。 静电纺丝技术制备的防粘连膜具有生物相容性良好的优势,褚薛慧等[34]利用静电纺丝的方法将壳聚糖制备成纳米纤维膜,并对肝细胞在壳聚糖纳米纤维电纺膜表面的活性与功能进行了研究,证实该纳米纤维电纺膜有较好的生物相容性和生物活性,无毒副作用,并且对肝细胞在其表面的黏附与生长非常有利,使得这种电纺膜在预防术后粘连中成为可能。 利用静电纺丝技术所制得的防粘连膜具有良好的组织黏附性,Chen等[35]通过静电纺丝技术制备聚乙二醇/聚己内酯纳米纤维膜,并用该膜进行防肌腱粘连实验,观察体外细胞黏附性,组织学和功能分析结果表明该电纺纳米纤维膜是一种有效的防肌腱粘连膜。 静电纺可吸收防粘连膜具有良好的柔软性,薛燕 等[36]在电压为8 kV、流速为0.8 mL/h、接收距离为 15.5 cm的参数条件下通过静电纺丝法用聚乳酸及改性材料制备防粘连纤维膜,并考察不同纤维膜在玻璃化转变温度(Tg)、力学性能、形貌及降解时间等方面的异同,结果显示静电纺丝技术制备的聚乳酸及其复合材料防粘连纤维膜具有良好的多孔结构与力学性能,避免了用传统浇铸法制备聚乳酸膜的缺点,满足了防粘连膜对于柔软性的要求,其断裂伸长率也显著提高,降解时间也明显缩短;韩志超等[37]在接收距离为12 cm,电压为 20 kV,流速为21 μL/min,温度为25 ℃等实验条件下对高分子材料聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物进行静电纺,制备出柔顺性良好的静电纺丝高分子防粘连纤维膜,该膜在液体环境中能保持良好的柔顺性以及物理形貌、断裂伸长率,适用于胸腔、腹腔、盆腔等部位的术后防粘连;同时韩志超等[38]在接收距离为7-15 cm,电压为10-35 kV,流速为10-30 μL/min等实验条件下利用静电纺丝技术对聚己内酯和聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物进行静电纺,制备出以聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物为功能层、聚己内酯为支撑基层的防粘连可吸收疝气补片,该产品在体内可防止术后粘连,同时促进细胞再生,减少瘢痕组织的生成,并具有力学支撑和组织重塑作用。 目前市面上的静电纺可吸收防粘连产品具有允许体液通过而降低感染的特点。例如疝修补片有效防止粘连的发生,允许体液等通过而避免积液现象的同时易实现无菌化生产。 许多静电纺防粘连膜均具有良好的黏附性能,同时具有可完全降解吸收、无刺激性以及降解时间速度可控等优点[39-41]。利用静电纺丝技术所发明的一种医用防粘连膜,不但克服已有技术的缺陷,而且无毒性,黏附性能好;采用静电纺丝法制得的防粘连组织修复膜,不但利于细胞的黏附和增殖,膜质地轻且柔软,可有效防止粘连,而且具有理想的修复效果;用静电纺丝技术制得的止血聚乳酸防粘连膜,具有双层结构,膜机械强度良好,使膜与创面有良好的黏附性从而易于固定,具有防粘连作用且有较好的止血功能,尤其适用于活动性出血的止血;还有一种神经术后防粘连膜,其制作简单,膜柔韧性好、防粘结能力强。 带细胞支架一类的防粘连医用膜产品具有较为完善的力学性能,促进创面愈合的同时能有效防止术后粘连的发生。例如部分可吸收的双层纤维膜疝气补片,其力学强度强、柔韧性好、良好的细胞亲和性,有效防粘连[42];一种用于医学手术中防止组织粘连的带细胞支架的医用膜,具有良好的生物相容性和力学性能,其多孔三维细胞支架能加快创面的愈合速率,显著降低粘连的发生。 综上所述,随着防粘连膜制备技术的日趋完善及防粘连膜在外科领域的广为应用,利用新兴的静电纺丝技术制备适宜的生物膜展现出了强大的优越性。"
| [1]侯丽华. SA/CS术后防粘连膜的制备及降解研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2012:1-52.[2]高春娟.术后防粘连材料的制备及性能研究[D]. 天津:天津大学, 2005:4-10.[3]凌沛学,管华诗.透明质酸及其衍生物防粘连的研究与应用[J].中国药学杂志,2005,40(20): 1527-1530.[4]曾莉,颜帅,李文林.国外抗腹腔粘连材料的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2014,27(12): 1315-1317.[5]Takahashi A, Suzuki Y, Suhara T, et al. In situ cross-linkable hydrogel of hyaluronan produced via copper-free click chemistry. Biomacromolecules. 2013;14(10):3581-3588.[6]Wallwiener M, Brucker S, Hierlemann H, et al. Innovative barriers for peritoneal adhesion prevention: liquid or solid? A rat uterine horn model. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(4 Suppl): 1266-1276.[7]王敏辉.天然高分子改性材料的发展及应用[J].新疆化工,2011 (3):4-6,25.[8]何乐,陈复生,刘伯业,等.天然高分子可降解材料的研究与进展[J].化工新型材料,2011,39(5):4-6.[9]常菁,刘万顺,韩宝芹.防粘连壳聚糖衍生物共混膜的生物学性质研究[J].功能材料,2008,39(4):651-655,659.[10]彭人勇,王志栋.PVA/MMT纳米复合材料的化学改性研究[J].塑料科技,2007,35(2):54-58.[11]Liu X, Hu GY, Gu HQ. Study on biocompatibility of cross-linked hyaluronic acid derivatives. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering(English Edition).2009;18(3):93-101.[12]卢凤琦,曹宗顺.生物降解性防术后粘连膜的实验研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,1996,13(4): 375-377.[13]杨红江,吕银祥,刘纪炎,等.防粘连膜预防腹腔术后肠粘连形成的临床研究[J].中国现代医生,2014,52(36): 113-115.[14]赵玉娟,肖桂勇,黄琳,等.壳聚糖理化、生物学特性及其产品安全性的研究进展[J].山东医药,2014,54(34): 93-97.[15]林红宁.壳聚糖膜剂致眼结膜充血不良事件分析[J].中国药物警戒,2011,8(5): 309-311.[16]史文娟,刘丽敏.防粘连膜在重度宫腔粘连综合治疗中的应用分析[J].中国医药科学,2015,5(10):76-78.[17]王亚,高卫东,卢雨正.织物柔软性的主客观评价[J].纺织学报, 2008,29(5):22-25.[18]马富平,石明.聚-DL-乳酸医用膜应用于腹部手术预防粘连的临床观察[J].中国医学工程,2012,20(4): 68-69.[19]黄启顺,王发斌,康浩,等. 聚-DL-乳酸可吸收性防粘连膜预防肌腱粘连的临床应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10): 990-991.[20]陈昕,朱维培.粘克®可吸收医用膜预防妇科术后盆腔粘连的临床观察[J].生物医学工程与临床,2015,19(3):285-287.[21]谭秀梅,何凯.粘连平腹腔灌注预防肠粘连的临床研究[J].中国社区医师,2010,12(21):103.[22]于吉财.粘连平在预防腹部手术后粘连的临床观察[J].现代医药卫生,2007,23(7):1024.[23]刘曦,岳卫华.医用可吸收防粘连膜产品的研究进展及基本要求[J].医疗装备,2014,27(4):5-8.[24]Jin SW, Ahn HB, Roh MS, et al. Efficacy of Seprafilm(®) graft with adhesiolysis in experimentally induced lid adhesion in rabbits. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013;6(1):44-49.[25]郝明磊,郭建生.国内外静电纺丝技术的研究进展[J].纺织导报, 2013(1):58-60.[26]邵自强,王飞俊,王文俊,等.纤维素混合醚酯的制备与静电纺丝性能[J].高分子通报,2010(11):65-70.[27]冯惠,方乃照,王建军,等.维生素对聚乙烯醇溶液静电纺丝性能的影响[J].合成纤维工业,2009,32(3):30-33.[28]Bagherzadeh R, Latifi M, Kong L. Three-dimensional pore structure analysis of polycaprolactone nano-microfibrous scaffolds using theoretical and experimental approaches. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(3):903-910.[29]Nguyen TH, Padalhin AR, Seo HS, et al. A hybrid electrospun PU/PCL scaffold satisfied the requirements of blood vessel prosthesis in terms of mechanical properties, pore size, and biocompatibility. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(14): 1692-1706.[30]丁彬.静电纺纳米纤维的可控制备及其在能源、环境领域的应用[C].成都:中国化学会第28届学术年会第4分会场摘要集,2012.[31]杨恩龙,王善元,李妮,等.静电纺丝技术及其研究进展[J].产业用纺织品,2007,25(8):7-10.[32]丁彬,俞建勇.静电纺丝与纳米纤维[M].北京:中国纺织出版社, 2011.[33]姚清华.RGD-重组蛛丝蛋白/聚乙烯醇电纺膜创面敷料的研究[D].福州:福建师范大学,2009.[34]褚薛慧,施晓雷,顾劲扬,等.壳聚糖纳米纤维电纺膜体外对肝细胞作用的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2010,29(1):144-149.[35]Chen CH, Chen SH, Shalumon KT, et al. Prevention of peritendinous adhesions with electrospun polyethylene glycol/polycaprolactone nanofibrous membranes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;133:221-230.[36]薛燕,刘超.静电纺丝法制备聚乳酸防粘连纤维膜的研究[J].橡塑资源利用,2015(2):26-28.[37]韩志超,许杉杉.柔顺性良好的静电纺丝高分子防粘连纤维膜:中国,CN201210444894.4[P].2016-07-27.[38]韩志超,许杉杉.防粘连可吸收疝气补片:中国, CN201210444936.4[P]. 2016-07-27.[39]毛箬青.静电纺PLGA防粘连膜的免疫学效应研究[D]. 兰州:兰州理工大学,2012.[40]颜静.明胶/PLLA复合纤维膜的制备及在角膜组织工程中的性能研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2012.[41]王群旺.丝素蛋白与聚丁二酸丁二醇酯复合超细纤维膜的制备及性能研究[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2010.[42]王颖初.聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)疝修补片的制备与性能研究[D].上海:东华大学,2014. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaoyang, Tang Tian, Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Repair and regenerative therapies of the annulus fibrosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1582-1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||